Your basket is currently empty!
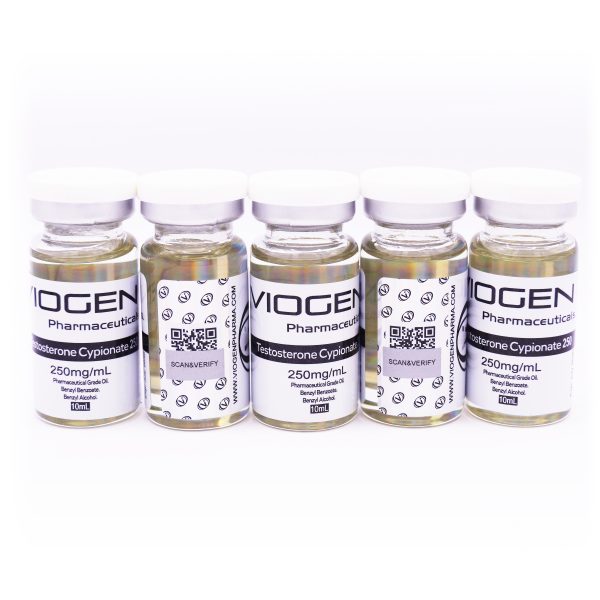
Testosterone Cypionate 250 – 5-vial x 10ml bundle (250mg/1ml)
£130.00
Testosterone Cypionate 250 – VIOGEN Pharmaceuticals
5x 1vial 10ml (250MG/1ML)
| Fast shipping | |
| Tested product |
In stock
Description
What is Testosterone Cypionate?
Testosterone Cypionate is a long-acting esterified form of testosterone, which is the primary male sex hormone and a naturally occurring anabolic-androgenic steroid (AAS). It is an injectable compound designed to deliver testosterone into the bloodstream gradually over an extended period. The cypionate ester attached to the testosterone molecule slows its release from the injection site, allowing for less frequent administration compared to short-acting forms such as testosterone propionate. Once in the bloodstream, the ester is metabolized, releasing free, active testosterone.
Testosterone plays a central role in numerous physiological processes. It regulates protein synthesis, nitrogen retention, red blood cell production, and muscle tissue maintenance. It also influences bone density, libido, mood, and overall energy levels. Testosterone Cypionate, as an exogenous source of this hormone, replicates the effects of endogenous testosterone but at a higher or more controlled dosage than the body naturally produces.
Medically, Testosterone Cypionate is primarily used in testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) for men with hypogonadism or low natural testosterone production. It restores normal hormone levels, alleviating symptoms like fatigue, low libido, mood swings, and decreased muscle mass. Its long half-life—approximately 8 days—makes it convenient for clinical administration, requiring injections every 1–2 weeks to maintain stable blood testosterone levels.
The chemical structure of Testosterone Cypionate is identical to endogenous testosterone, with the only difference being the cypionate ester attached to the 17-beta hydroxyl group. This ester increases the molecule’s lipophilicity, allowing it to remain in the muscle tissue at the injection site and be slowly released into circulation. This mechanism ensures a steady hormonal profile, avoiding the peaks and troughs associated with shorter-acting testosterone esters.
Testosterone Cypionate is highly anabolic, promoting protein synthesis and nitrogen retention in muscle tissue. It is also androgenic, meaning it supports the development of male secondary sexual characteristics such as facial and body hair, deepening of the voice, and increased libido. These dual effects—anabolic and androgenic—make testosterone Cypionate a powerful and versatile hormone within therapeutic and enhancement contexts.
Pharmacokinetically, after intramuscular injection, testosterone Cypionate is absorbed into the bloodstream gradually. Peak serum levels typically occur within 24–48 hours, and the effects last for approximately 7–10 days. The gradual release allows for consistent androgen receptor activation, supporting both physiological and anabolic processes continuously over time.
Testosterone Cypionate is sometimes compared to other long-acting esters, such as testosterone enanthate. While both have similar half-lives and effects, subtle differences in pharmacokinetics can affect dosing schedules and individual response. Overall, Testosterone Cypionate is considered effective, stable, and well-tolerated when administered correctly.
Its advantages in medical and controlled-use contexts include precise dose management, predictable serum levels, and reliable anabolic and androgenic activity. However, misuse or unsupervised use can lead to hormonal imbalances, side effects, and suppression of natural testosterone production. Understanding what Testosterone Cypionate is and how it functions is essential before considering its application.
Cycle and Dosage
Testosterone Cypionate is typically used in structured cycles to optimize results while minimizing potential side effects. For therapeutic purposes such as testosterone replacement therapy (TRT), the cycle is continuous, with consistent doses administered every 1–2 weeks to maintain physiological hormone levels. In non-medical contexts, cycles are usually 8–12 weeks, followed by post-cycle therapy (PCT) to restore natural testosterone production and manage estrogen-related side effects.
For performance or enhancement purposes, typical dosages range from 250 mg to 600 mg per week, divided into 2–3 injections to maintain stable blood testosterone levels and avoid significant peaks and troughs. Some advanced users may increase the dosage, but higher amounts considerably increase the risk of side effects. Proper cycle planning includes consideration of:
- Cycle length: 8–12 weeks is common for beginners or intermediates
- Injection frequency: splitting the weekly dose helps stabilize serum levels
- Ancillary drugs: aromatase inhibitors (like anastrozole) can prevent estrogenic side effects
- Post-cycle therapy: SERMs (Tamoxifen or Clomiphene) help restore endogenous testosterone production
Adherence to a carefully planned cycle is crucial to balancing effectiveness and safety.
Pros of Testosterone Cypionate
Testosterone Cypionate provides several benefits due to its anabolic and androgenic effects. Key advantages include:
- Muscle growth: Increases protein synthesis and nitrogen retention, facilitating lean mass gain.
- Strength improvement: Enhances muscular power and recovery, enabling higher training intensity.
- Enhanced recovery: Reduces fatigue and accelerates tissue repair, supporting more frequent and intense workouts.
- Improved red blood cell production: Enhances oxygen delivery, potentially improving endurance and energy levels.
- Positive mood and libido effects: Restores energy, motivation, and sexual health in individuals with low testosterone.
- Bone and joint support: Helps maintain bone density and joint health, reducing the risk of injury.
These benefits make Testosterone Cypionate highly effective for restoring hormone balance and supporting physiological optimization.
Cons and Side Effects of Testosterone Cypionate
Despite its benefits, Testosterone Cypionate carries potential risks, particularly when used at higher doses or without medical supervision. Key concerns include:
- Estrogenic side effects: Aromatization of testosterone to estrogen may cause gynecomastia, water retention, bloating, and elevated blood pressure.
- Androgenic side effects: Acne, oily skin, increased body hair, and male-pattern baldness in genetically predisposed individuals.
- Cardiovascular effects: Altered cholesterol profile (decreased HDL, increased LDL), potential for hypertension, and increased risk of heart disease with prolonged high-dose use.
- Endocrine suppression: Exogenous testosterone suppresses natural testosterone production, leading to testicular atrophy and reduced fertility without proper PCT.
- Mood and behavioral changes: Irritability, aggression, and mood swings may occur, especially at higher doses.
- Injection-related issues: Pain, swelling, or infection at injection sites if sterile technique is not followed.
These side effects can be minimized through careful dosing, monitoring, use of ancillary drugs, and post-cycle therapy, but they cannot be completely eliminated.
In conclusion, Testosterone Cypionate is a potent, long-acting testosterone ester that provides significant anabolic and androgenic effects. When used responsibly with proper cycle planning, dosing, and post-cycle therapy, it offers substantial benefits in terms of muscle growth, strength, recovery, and overall well-being. However, misuse or unsupervised use increases the risk of estrogenic, androgenic, cardiovascular, and endocrine side effects, making careful planning and monitoring essential for safety.
What is Testosterone Cypionate?
Testosterone Cypionate is a long-acting esterified form of testosterone, the primary male sex hormone and an anabolic-androgenic steroid (AAS). It is administered via intramuscular injection, allowing testosterone to be released gradually into the bloodstream. The cypionate ester prolongs the hormone’s half-life, enabling less frequent injections compared to shorter-acting esters. Once metabolized, the ester releases active testosterone, which exerts both anabolic (muscle-building) and androgenic (male characteristic-promoting) effects.
This hormone regulates multiple physiological processes, including protein synthesis, nitrogen retention, red blood cell production, bone density, libido, energy, and mood. Medically, it is primarily used in testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) to alleviate symptoms of hypogonadism or low testosterone. Its pharmacokinetics provide stable blood levels for approximately 7–10 days per injection, reducing fluctuations and optimizing hormonal activity.
The chemical structure is identical to endogenous testosterone, except for the cypionate ester attached to the 17-beta hydroxyl group. This ester increases lipophilicity, slowing release from the injection site and allowing for consistent serum testosterone levels. Compared to shorter esters like propionate, Cypionate offers more convenient dosing schedules and stable hormone profiles.
Testosterone Cypionate is highly effective in promoting protein synthesis and nitrogen retention in muscle tissue, while also supporting androgenic functions such as facial and body hair growth, vocal changes, and libido. Its dual anabolic-androgenic nature makes it a versatile hormone with both therapeutic and performance-related applications. Proper administration ensures predictable and controlled effects, while misuse can lead to hormonal imbalances, suppression of natural testosterone production, and a range of side effects.
FAQ: 10 Most Common Questions About Testosterone Cypionate
- How does Testosterone Cypionate work?Once injected, the cypionate ester is metabolized in the bloodstream, releasing free testosterone. This hormone binds to androgen receptors in tissues such as muscle, bone, and liver. Binding activates transcription of genes responsible for protein synthesis, nitrogen retention, and other anabolic processes. Testosterone also interacts with the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal (HPG) axis, regulating endogenous hormone production and influencing physiological functions like mood, libido, and red blood cell production.
- What is the typical medical dosage?In TRT, doses range from 50–200 mg every 1–2 weeks, administered intramuscularly. The objective is to maintain serum testosterone within a normal physiological range. Blood work is essential to monitor hormone levels and adjust dosage accordingly, ensuring efficacy while minimizing side effects.
- What is the typical dosage for enhancement purposes?For non-medical use, doses usually range from 250–600 mg per week. Some advanced users may use higher doses, but these significantly increase the risk of adverse effects. Injections are often split into two per week to maintain stable testosterone levels, reducing peaks and troughs. Duration of use is commonly 8–12 weeks, followed by post-cycle therapy (PCT) to restore natural testosterone production.
- How long does Testosterone Cypionate stay active?Its half-life is approximately 8 days, providing stable blood testosterone levels for 7–10 days per injection. Peak levels are typically reached within 24–48 hours. The long half-life allows less frequent dosing and steady receptor activation, supporting both anabolic and androgenic effects over time.
- What are the main benefits?Key benefits include:
- Increased muscle mass and strength through enhanced protein synthesis and nitrogen retention
- Improved recovery and reduced fatigue
- Enhanced red blood cell production and oxygen delivery
- Improved libido, sexual performance, and mood
- Support for bone density and joint health
These effects make Testosterone Cypionate effective for restoring hormonal balance and promoting physiological and performance improvements.
- What are the side effects?Common side effects include:
- Estrogenic: gynecomastia, water retention, bloating due to aromatization
- Androgenic: acne, hair loss in predisposed individuals, increased body hair
- Cardiovascular: changes in cholesterol (lower HDL, higher LDL), elevated blood pressure
- Endocrine: suppression of natural testosterone production, testicular atrophy without PCT
- Other: mood swings, aggression, rare liver strain
Monitoring, correct dosing, and use of ancillary drugs such as aromatase inhibitors or SERMs can help manage these risks.
- How is a typical cycle structured?Cycles often last 8–12 weeks. Weekly dosages are divided into multiple injections to maintain stable serum testosterone levels. After completing the cycle, PCT is recommended to restore endogenous testosterone production and mitigate estrogenic side effects. Cycle length and dosing should consider user goals, tolerance, and safety.
- Can Testosterone Cypionate be stacked with other compounds?Yes, it is often combined with other anabolic steroids for synergistic effects. Commonly paired compounds include nandrolone, boldenone, or trenbolone. Stacking increases anabolic potential but also raises the risk of side effects, particularly estrogenic, cardiovascular, and endocrine complications.
- How should injections be administered?Testosterone Cypionate is given intramuscularly, typically in the gluteal muscle, thigh, or deltoid. Sterile technique is essential to avoid infection or injection-site complications. Some users divide weekly doses to reduce peaks and maintain a more stable hormonal environment. Rotation of injection sites is recommended to minimize tissue irritation.
- Is Testosterone Cypionate legal and safe?Legally, it is prescription-only in most countries, approved for TRT and other medical indications. Non-prescribed use may be illegal. Safety depends on proper dosing, monitoring, and PCT. High-dose or prolonged non-medical use increases risks of cardiovascular, endocrine, and androgenic side effects. Regular blood work and medical supervision are recommended to minimize potential health risks.